Benefits of natural ceramides in the Rosette AK Series

The role of ceramide
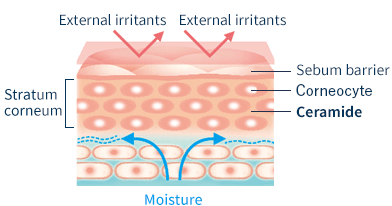
The surface of the skin has a protein layer called the stratum corneum. The spaces between cells in the stratum corneum contain a lipid called ceramide. Ceramide is an intercellular lipid that is created during the process of cell turnover, and contains about 30% moisture. It acts as the glue that holds cells together. When the skin is rich in ceramide, the stratum corneum stays moist for hydrated, dewy skin.
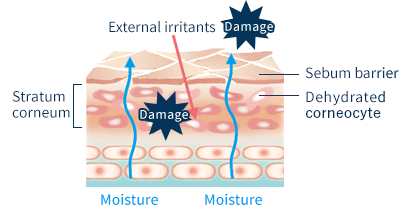
Atopic dermatitis, on the other hand, is known to involve extreme ceramide deficiency. We also lose ceramide as we age, causing moisture to readily evaporate from the surface of the skin during the colder months when we don’t sweat.
Ceramide keeps the outer layers of skin healthy and serves a so-called barrier function. When the epidermis is healthy, it locks in moisture and keeps antigens (allergy-causing agents like mites and dust) from infiltrating the skin. It also protects against more general environmental irritants. However, because people with atopic dermatitis lack sufficient ceramide, the barrier function is weakened. Moisture readily escapes from within the skin, drying it out and allowing antigens to enter. Once these irritants have penetrated the skin, they trigger an allergic reaction that results in various forms of inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis is also referred to as “extremely dry skin”. For this reason, in addition to pharmaceutical treatments to inhibit skin inflammation, it is important that patients follow a skincare regimen that focuses on replenishing the ceramides needed to alleviate dry skin and enhance barrier function.
What is the natural ceramide in the Rosette AK Series?
To ensure that our products are safe to use even by patients struggling with atopic dermatitis, the Rosette AK Series contains horse sphingolipid, which is a natural ceramide extracted from fresh spinal marrow of healthy horses. This natural ceramide contains over 70% galactosylceramide as well as an excellent balance of sphingomyelin, phosphatidylethanolamine , lecithin, cholesterol, and other nutrients to enhance skin’s barrier function and help it retain moisture.
Benefits of natural ceramides in the Rosette AK Series
※Source: Rosette R&D
Galactosylceramide, the main component of the natural ceramide, increases the protein expression levels of ceramide synthesis related enzymes and ceramide levels.
Galactosylceramide (GalCer) is a sphingolipid, which consisting of ceramide and galactose. GalCer significantly increases the ceramide content of the stratum corneum, via significantly up-regulates gene and/or protein expression levels of ceramide synthesis-related enzymes.
- Galactosylceramide is topically applied to the skin.
- GalCer increases the protein expression levels of several ceramide synthesis-related enzymes.※1
※1 β-glucocerebrosidase, glucosylceramide synthase, sphingomyelin synthase, ceramide synthase 3, fatty acid elongase 4 - GalCer stimulates ceramide synthesis in the stratum corneum.
- GalCer increases various types of ceramide compositoin※2 in the epidermis and promotes the formation of lamellar structures.
※2 Ceramide EOS, Ceramide NS/NDS, Ceramide AP, Ceramide NP, Ceramide AH
Galactosylceramide reconstructs the lamellar structure of intercellular lipids.
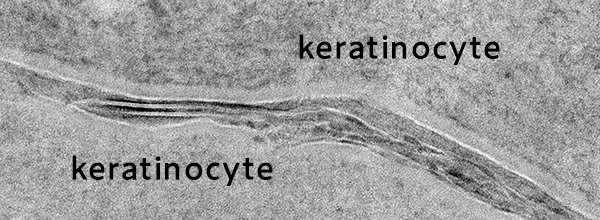
(no GalCer treatment)
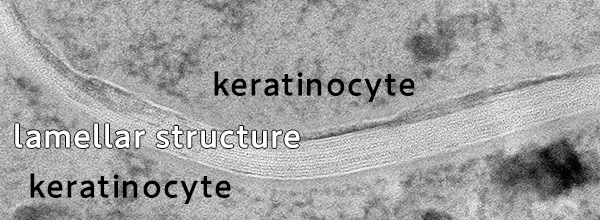
(with 0.5% GalCer treatment)
While rough skin without GalCer treatment was observed to have a disordered lamellar structure, the treatment of rough skin with 0.5% GalCer promoted the construction of the lamellar structure in the stratum corneum. (Rough skin was induced by SLS treatment on a three-dimensional skin model. Rough skin was treated with GalCer once a day for 4 days and observed by electron microscope.)
